 EPS is a closed cell, lightweight, foamed plastic which has a compression strength between 10 to 33 PSI for most construction applications. Applied in roofing, foundations, and walls. EPS has a successful history of efficient use in industrial, commercial, residential and cold storage buildings.
EPS is a closed cell, lightweight, foamed plastic which has a compression strength between 10 to 33 PSI for most construction applications. Applied in roofing, foundations, and walls. EPS has a successful history of efficient use in industrial, commercial, residential and cold storage buildings.
EPS insulation (1 lb. per cubic foot) provides a typical R-value of 3.9 per inch at mean temperature of 75° F. The R-value of EPS insulation is permanent because the cellular structure of EPS contains only stabilized air. It's R value will not decrease as it ages.
Exterior Sheathing
- Meets or exceeds current energy conservation design standards without increasing stud width.
- Reduces air infiltration and heat loss through framing; slows convective looping.
- Corner bracing required for non-structural sheathing.
- Foil-faced EPS with air space can provide additional R-value; retards radiant heat flow.
- Peforated foil promotes breathability.
- Elimiates need for extra-deep framing.
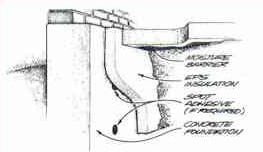 Perimeter Insulation
Perimeter Insulation
- Select strength and thickness to meet loading and thermal requirements.
- Long-term resistance to slab edge heat loss
Eave Vents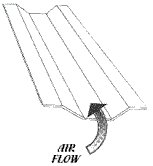
- Allow air to enter at the eave and move out hot, energy-robbing attic air in summer and damaging attic air in the winter.
- Proper roof ventilation eliminates the potential damaging ice build-up at eaves and valleys.